Precision In Neurosurgery: How Neurosurgeons Use MRI and CT Scans For Accurate Diagnosis
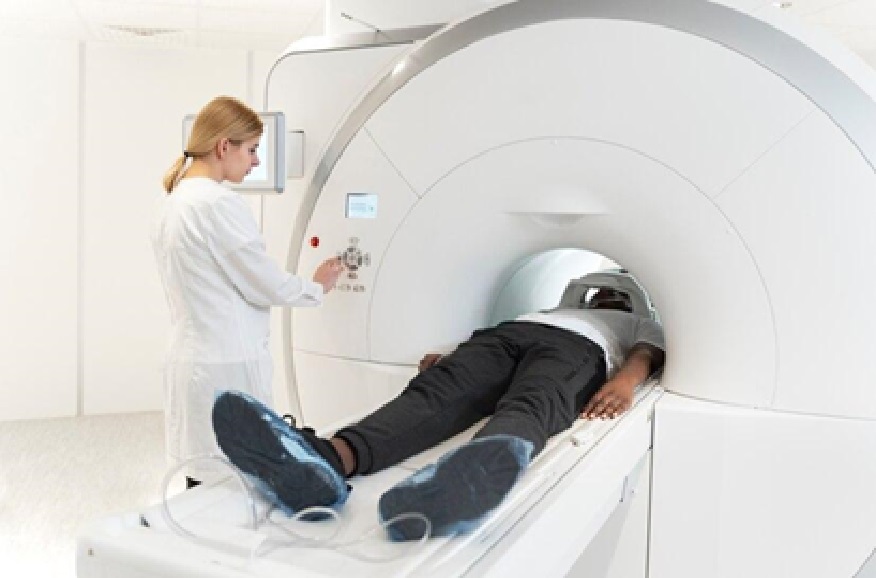
In neurosurgery, precision is crucial. Neurosurgeons use MRI and CT scans to make accurate diagnoses and plan treatments. MRI creates detailed images of soft tissues, helping identify tumors and blood clots, while CT scans provide cross-sectional images to locate abnormalities. Both techniques enhance surgical planning and outcomes, ensuring patient safety and confidence in complex procedures. In neurosurgery, precision is key to success.
Importance Of Accurate Diagnosis In Neurosurgery
Accurate diagnosis in neurosurgery is vital due to the complex nature of the nervous system. Misdiagnoses can lead to inappropriate treatments, causing irreversible damage. Neurosurgeons depend on precise imaging to detect abnormalities affecting critical functions like movement, sensation, and cognition. Conditions like brain tumors or traumatic injuries require urgent attention, and accurate diagnosis guides surgical intervention, treatment plans, and ongoing care. Furthermore, a correct diagnosis helps patients understand their condition, reduces anxiety, and enables active participation in their treatment, ensuring better clinical and emotional outcomes for patients and families.
Role Of MRI Scans In Neurosurgical Diagnosis

MRI plays a crucial role in neurosurgery by providing non-invasive, high-resolution images of soft tissues like the brain and spinal cord without ionizing radiation. It helps neurosurgeons identify conditions such as tumors, degenerative diseases, and structural abnormalities, crucial for surgical planning. MRI differentiates between gray matter, white matter, and cerebrospinal fluid, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Advanced techniques like diffusion tensor imaging and functional MRI further improve brain connectivity and activity assessments. MRI also aids in monitoring post-operative changes and tracking the progression of neurological conditions, enabling timely interventions when necessary.
Benefits And Limitations Of MRI Scans In Neurosurgery
MRI scans offer significant benefits in neurosurgery. They provide high-resolution images of soft tissues without radiation and are safe for repeated use, especially in younger patients. They can detect subtle tissue changes and be tailored to focus on specific areas using contrast agents to enhance the visibility of tumors or lesions. Functional MRI also helps assess brain activity, aiding in surgery planning for critical regions involved in speech, movement, or sensory functions.
However, MRI has limitations, including time consumption and the need for patients to remain still, which can be difficult for those with anxiety or claustrophobia. While MRI excels in soft tissue imaging, it may not provide enough detail for bony structures, necessitating complementary techniques like CT scans for a comprehensive view.
Role Of CT Scans In Neurosurgical Diagnosis
CT scans play a complementary role in neurosurgery, offering rapid imaging, which is essential in emergencies like traumatic brain injuries or strokes. They excel at visualizing bony structures, making them invaluable for assessing skull fractures and identifying sources of bleeding. CT scans are also enhanced with contrast agents to visualize tumors, lesions, or vascular structures, aiding in surgical planning. CT angiography, for example, provides detailed images of blood vessels, essential for procedures involving vascular anomalies like aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations.
Benefits And Limitations Of CT Scans In Neurosurgery
CT scans are crucial in neurosurgery, offering rapid imaging for emergencies like strokes or traumatic brain injuries. They excel at visualizing bony structures and assessing skull fractures and osseous abnormalities. CT scans are widely available in emergency departments, ensuring quick access to diagnosis and treatment. However, ionizing radiation is a concern, particularly for younger patients or those requiring multiple scans. Additionally, CT may not provide as detailed soft tissue imaging as MRI, making it necessary to use both modalities for comprehensive evaluation.
Integration Of MRI and CT Scans In Neurosurgical Planning
Integrating MRI and CT scans in neurosurgical planning significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy and surgical outcomes. MRI provides detailed soft tissue images, while CT excels in visualizing bony structures. For instance, in brain tumor cases, MRI helps define the tumor’s size and location, while CT evaluates the involvement of the skull. By combining these modalities, surgical planning becomes more precise. Moreover, advanced surgical navigation systems that fuse MRI and CT data at Tellica Imaging (https://tellicaimaging.com/) provide real-time guidance, improving precision and minimizing complications by offering a 3D view of complex anatomical structures. Tellica Imaging provides state-of-the-art imaging services that further optimize these processes in neurosurgery.
Advanced Technologies For Precise Neurosurgical Diagnosis
As technology evolves, new tools like intraoperative imaging, robotic assistance, and augmented reality are revolutionizing neurosurgical precision. Intraoperative MRI provides real-time imaging during surgery, helping surgeons assess tumor resection and monitor complications. Robotic systems enhance dexterity and accuracy, minimizing human error. Additionally, augmented reality overlays imaging data onto the surgeon’s field of view, offering real-time guidance and improving spatial awareness, leading to better surgical outcomes.
Conclusion: The Future Of Precision In Neurosurgery
The future of precision in neurosurgery is bright, with continued advancements in imaging technologies and surgical techniques. As neurosurgeons increasingly integrate MRI and CT scans into their practice, they can expect to see improvements in diagnostic accuracy, surgical planning, and patient safety. The ability to visualize the intricate structures of the brain and spinal cord in exceptional detail will only enhance the effectiveness of neurosurgical interventions.
Moreover, the ongoing development of innovative technologies, such as intraoperative imaging, robotic assistance, and augmented reality, promises to refine the precision of neurosurgical practices further. These advancements will improve outcomes and empower surgeons to tackle even the most complex cases confidently.
In summary, the role of MRI and CT scans in neurosurgery cannot be overstated. These imaging modalities are the backbone of accurate diagnosis and successful surgical outcomes. As the field continues to evolve, the commitment to precision will remain at the forefront of neurosurgery, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care.













